3D PRINTING
DESCRIPTION
3D printing, also known as stereoscopic printing, additive manufacturing, and additive manufacturing, can refer to any process of printing 3D objects. 3D printing is primarily a continuous process of adding and layering raw materials under computer control. 3D printed content can be derived from 3D models or other electronic data, and the printed 3D objects can have any shape and geometric characteristics. 3D printers are a type of industrial robotics.
The original meaning of the term "3D printing" refers to the process of sequentially depositing materials onto a powdered layer of inkjet print heads. Recently the term has been expanded to include a wide range of technologies such as extrusion and sintering processes. Technical standards generally use the term "additive manufacturing" to convey this broad meaning.


YEAR
2021
MONTH
OCTOBER
PLATFORM
Spark 3D Printing Cloud
Modeling
Finished
3D printed models can be generated using computer-aided design software packages or 3D scanners. The process of manually gathering the geometric data needed to produce a 3D image is similar to that of plastic arts such as sculpture. With 3D scanning, electronic data about the shape and appearance of real objects can be generated and analyzed. Based on the data obtained from the 3D scan, a 3D computer model of the scanned object can be generated.
No matter which 3D modeling software is used, the generated 3D model (usually in .skp, .dae, .3ds or other formats) needs to be converted into a format that can be read by printers such as .STL or .OBJ.
Printing
Before printing 3D models using STL format files, a "flow error" check, often called a "correction" step, needs to be performed. The STL file "correction" is especially important for models obtained using 3D scanning, as such models often have a large number of flow errors. Common flow errors include surfaces that are not connected to each other or gaps in the model. netfabb, Meshmixer, or Cura and Slic3r are all common correction software.
Although the resolution of 3D printing can meet the requirements of many products, there is still room for upward mobility. The way to do this is to first print a slightly larger model than required at standard resolution, and then remove the excess material using a high-resolution reduction program. This results in a more accurate 3D model.Some of the polymers available for printing allow for a smooth surface when finished and are improved using a chemical vapor phase process. Some additive manufacturing techniques allow the use of multiple materials in the printing process. These technologies are capable of both color and mixed-color printing and do not necessarily require painting. Some printing techniques require internal supports to build cantilever features. These supports must be mechanically removed or dissolved at the completion of printing. All commercially available metal 3D printers include the ability to cut away metal parts from the metal substrate after deposition, and GMAW 3D printing has a new process for removing aluminum parts with a hammer to modify the substrate surface.
HOW TO START 3D MODELING

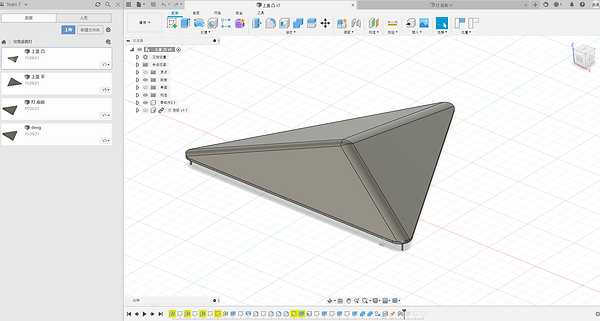
-
Draw the target printed object using Fusion modeling software
-
Exporting .stl format files
01 Modeling
-
Uploading model data to the spark 3d printing cloud server
-
Set the corresponding parameters
-
Choosing the right 3d printer
02 Print parameter settings


03 Printing
-
Print system to printer connection
-
Platform level calibration
-
The distance between the printhead and the platform is calibrated by means of a calibration sheet. Calibration is complete when there is some resistance to pulling the calibration sheet by hand
-
Model import
-
Set printing parameters
-
Start printing

04 Finished
-
Assembly,
-
Through 3D printing we have designed a touchable breathing light that changes color when a button is pressed.